






















Design, verification & testing, including documentation packs, work instructions, tools & testing equipment and modular work cells.

Design, supply chain and operational compliance systems incorporate relevant ISO, EN and UIC standards.

Like-for-like parts manufactured to OEM specification or better and/or sourced from parallel OEM supply chain.




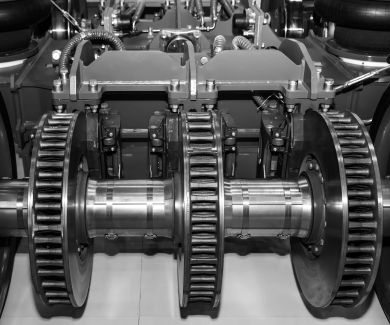
In meeting and exceeding original equipment specifications, Trovon’s high performance
reengineering processes facilitate: improved component performance, extended service
intervals, prolonged asset life, supply chain efficiencies, superior fleet availability, penalty
mitigation and safety.






Trovon’s AI solution analyses, optimses and learns from data to augment human intelligence in the prediction of future asset maintenance requirements and the optimisation and automation of processes.

Chief Operating Offier & Managing Director

Business Development Manager,
Australia & New Zealand

Head of Operations, SEA

General Manager Sales, Australia













Rolling stock is transit vehicles used for support services,including powered and unpowered vehiclessuch as locomotives, railcars, freight cars, passenger cars, ferry boats, trolley cars, buses, vans and cars. The term ‘rolling stock’ is often used in the rail transport industry and refers to railway vehicles or wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways. Rolling stockhas also been expanded to includeall engines and carriages that are used on a railway. The term‘rolling stock’ is defined in the Buy America regulations (49 CFR Part 661.3). The word ‘stock’ is often referred to as inventory or liquid assets. Rolling stock can also be referred to as the value of the vehicle,i.e. locomotive or railcars,based on asset performance and component life. Rolling stock is different to fixed stock within the rail transport industry. Fixed stock is a collective term for the track, signals, station and any fixed asset necessary to operate a railway that doesn’t ‘roll’ or ‘move’.
Braking Systems asset management includes:
HVAC asset management includes:
Train door asset management includes:
Dampers & suspension asset management include:
Air generation & treatment units (AGTU) asset management includes:
Rail assets are the transit vehicles used for support services, including both powered and unpowered vehicles such as locomotives, railcars, and freight cars. Rail assets also extend to the maintenance of way equipment, including all the engines and carriages used on a railway, such as the Braking Systems, HVAC, doors, dampers & suspension and air generation & treatment units (AGTU). Rail assets, also known as Rolling Stock, are often used in the rail transport industry and refer to the railway or wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways.
The 4 four principal types of rolling stock are:
Rail management is very important as it informs you about your rolling assets’ efficiencies and life cycle. Rail management helps gather large amounts of information and then analyses the data to provide valuable information on flagged actionable jobs. The jobs must then be completed to ensure that all subsystems work safely and reliably alone and when combined as complete systems. In addition, rail management checks that equipment is operating efficiently and reliably to ensure that operational service availability remains at the high levels demanded by asset operators.
Rail management is essential to help improve component performance, extended service intervals, prolonged asset life, help with supply chain efficiencies and penalty mitigation and safety. In addition, rail management can ensure more efficient use of labour and materials during maintenance and repair, which helps cut costs and speeds up maintenance and repair activities. Rail management can also reduce the input energy and emissions required to produce replacement equipment, reduce waste generated by the disposal of the existing equipment, and extend the life of the components to enhance the asset value.
During condition-based assessments, a rail management professional or engineer will review fleet technical maintenance plans and optimise component overhaul intervals based on vehicle usage data and component condition.
Rail management is fundamentally important to assist with rolling asset product improvements. The culmination of engineering services and component design modifications helps improve life cycle cost, optimise performance, increase life, reduce maintenance costs, and provide a better return on investment.
